Table of Contents
- Varieties Of Basmati & Non-Basmati Rice
- Features Of Finest Quality Paddy
- How Rice is Processed Step By Step Or Multistage Processing
- Warehousing
Processing is an essential part of the production of rice, so how rice is processed and stored by basmati rice millers. The fundamental target of a rice processing framework is to eliminate the husk and the grain layers and produce a bowl of delicious rice to serve that is adequately processed and free from chemicals.
Varieties Of Basmati & Non-Basmati Rice
Basmati rice is known as the Queen of Fragrance, and it is one of the best rice exported by the Indian Basmati Rice Exporters and Millers.
The basmati rice has lots of range of varieties supplied in the Middle East and Gulf Regions. The quality of rice is supreme with additive nutritional benefits.
The paddy of the rice is processed carefully, which enhance the nutritional benefits. Basmati rice is a bowl of long grain rice and has pointy ends.
The rice has a unique aroma and authentic fragrance, which is enhanced by the milling process also.
The varieties of Basmati and non-basmati rice are:
Basmati rice varieties are:
· 1121 rice
· Pusa rice
· 1401 rice
· 1509 rice
· Sugandha rice
· Traditional rice
Non-basmati rice varieties are:
· PR11 rice
· PR14 rice
· Sharbati Rice
· IR 64/36 rice
These are varieties of Basmati and non-basmati rice, which the Indian rice millers export after the paddy is finely milled or processed.
Some of the varieties are hybrid, which makes the combination of perfect taste and texture.
Non-basmati rice varieties are demanded over African Regions like Nigeria, Benin, Ghana, Senegal, Gambia, Guinea, Libya, Angola, Kenya, Ethiopia, Somalia, Tanzania, etc.
The cultivation of non-basmati rice is in the Northern & Southern states of the Indian subcontinent like Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Kolkata, Haryana, Punjab, and Himachal Pradesh.
Features Of Finest Quality Paddy
The paddy should at the proper moisture and ensure that it will be at the suitable water level, i.e., 14% with high purity.
Characteristics of a quality paddy
1. Uniformly develop kernels
2. Equal size and shape
3. Free from cracks
4. Free of half-filled grains
5. No foreign substances like stones and weeds present
6. High processing
7. High head rice recovery
8.No discolouring
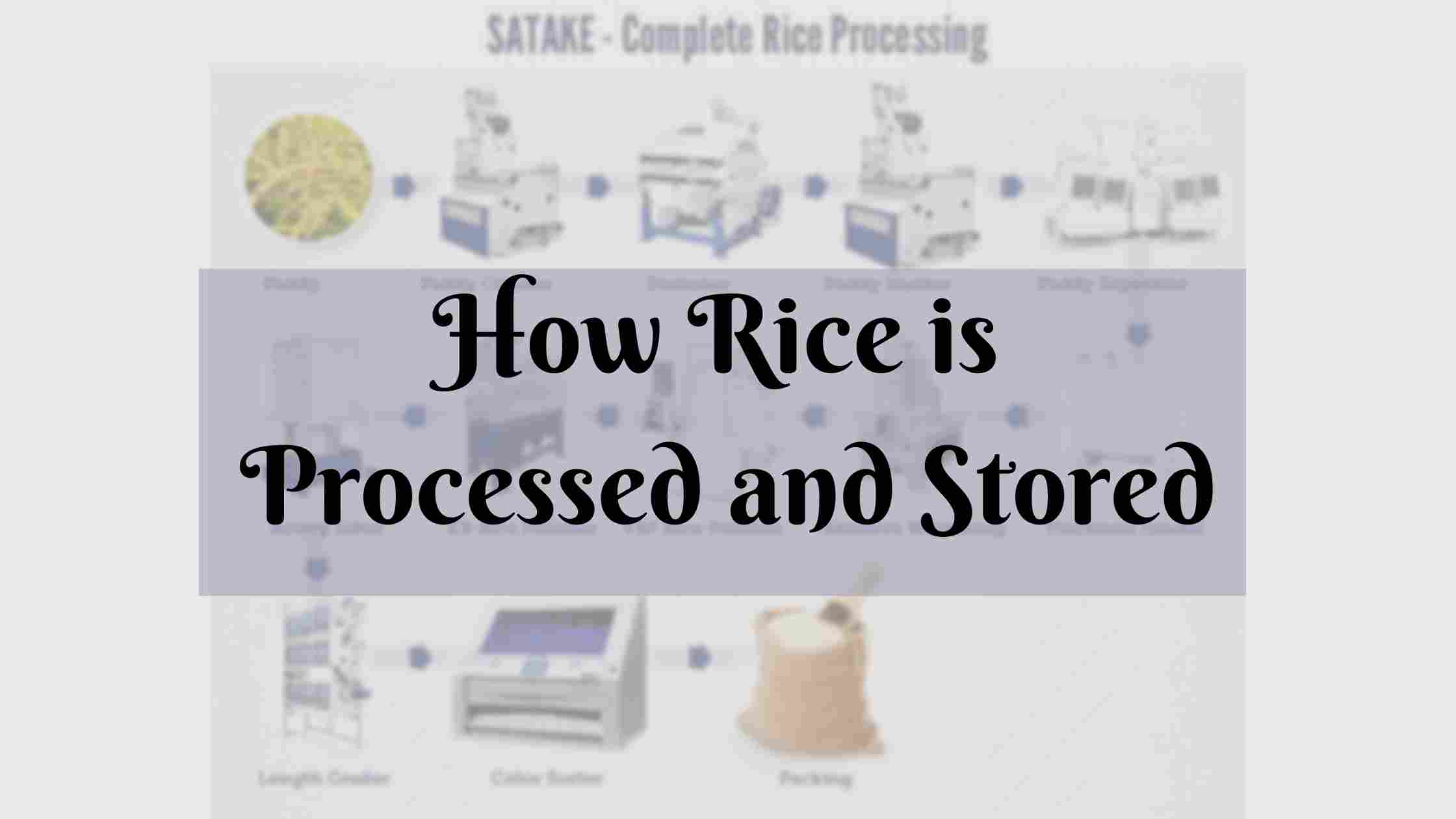
A rice processing framework can be basic steps to be followed:
- One-step processing -husk and wheat removal are done in one pass.
- Two-step measures -eliminating husk are done independently.
- Multistage processing -it goes through various typical preparing steps include:
1. Pre-cleaning
2. Dehusking or dehulling
3. Paddy separator
4. Brightening and polishing
5. Grading
6. Weighing of rice
How Rice is Processed Step By Step Or Multistage Processing
This process of paddy is mainly to expand its dietary benefit, and this cycle is called parboiling. It decreases breakage and even changes the flavour of cooked rice.
- Pre-cleaning technique: for fulling the high processing method, pre-cleaning the rice is vital. If not done as expected, the fines in the rice can make tidy and can decrease the flow of air through the rice grain. In addition, De-stoning is done to eliminate undesired stones present in the rice with the help of a gravity separator or a de-stoner.
- De-Husking or Dehulling: The step combines paddy into elastic rolls, circulating in inverse bearings at various speeds. The sheer power is created on the hull’s surface as the straight inside force is put on the elastic roll.
- Paddy Separation: The outside of a rice grain is smooth, though the outside of the paddy is harsh. Paddy separator utilizes this distinction in surface to outbreak rice from paddy.
- Brightening and Polishing: Rice polisher is utilized to clean the exterior of the rice. The components which decide the degree of whiteness are the spiral speed of the stone wheels, the network size of the stones, and the outside force on the power source of the brightening machine. The rice has been polished properly.
- Sorting: Sorting is the method that removes any foreign material, discolors rice and broken grain variety. With the latest technology of Buhler Optical Sorting Technology, the sorted process is easier than sorting rice by hand.
- Grading: Grading aims to analyze the rice, whether the head or broken rice grain, using the image. The main two steps followed in grading are sorting and assigning the grade. This method is for determining the quality of rice.
- Weighing of rice: Gauging and stowing machines are then used to weigh, pack and estimate that rice is precisely packed in the moisture-proof bags and sold as per the requirements.
Warehousing
The warehouse is required for safe storage to protect grain from uncertain climatic conditions, moisture, rodents, insects, and many microorganisms.
The husk gives some protection against insects and helps to prevent quality deterioration. Therefore, it is suggested that rice is stored in a paddy structure instead of processed rice to keep it healthy and safe from germs and other disinfectants.
Remarkable store frameworks include:
1. Security from bugs, rodents, and birds.
2. Assembling and discarding the unwanted paddy.
3. Effective utilization of room.
4. Stock maintenance and execution.
5. Avoidance of moisture entering the grain after drying.
Safe storage of rice for longer shelf life is done under these conditions:
- Grain is kept up at moisture levels of 14% or less
- Grain is shielded from bugs, rodents, and birds
- Grain is protected from re-wetting by a monsoon or absorbs moisture from the surrounding air
Great cleanliness in the grain store is significant in keeping up with grain from infection-free. To keep up with great cleanliness away:
- Keep store regions clean. It implies clearing the floor, eliminating spider webs and residue, and gathering and eliminating any grain disclosure.
- Clean extra spaces after they are exhausted, and this might include showering dividers and wooden beds with an insect poison before utilizing them once more.
- They are placing rodent traps and boundaries in drying and capacity regions.
- The grain stored has to be supervised twice a week to keep them pest-free and germ-free.